Simplify donor selection with HLA Typing test for the best match.
Request a Call Back
Thank you for your interest and sharing the details with us.
Our team will reach out to you on priority.
Team MedGenome
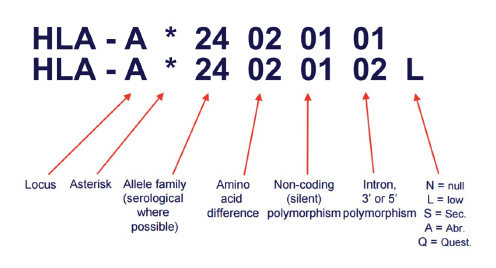
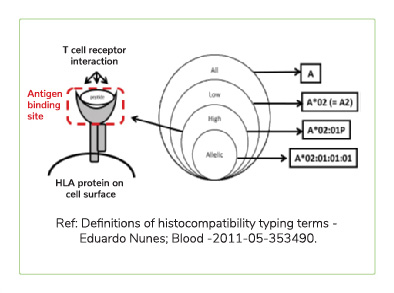
A next generation sequencing based test that helps find the best match for donor selection in allogenic organ and tissue transplant. Major Histocompatibility complex is Group of genes coding for a set of host surface molecules that bind to peptide fragments derived from pathogens and foreign antigens and display them on host cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T cells. It is also called as Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA). It Serves as a unique identification marker for every individual. In organ and tissue transplantation, HLA antigens of the donor identified as invaders by the recipient,causing rejection. Careful selection of the matched donor and recipient critically affect the outcome of transplantation.
During bone marrow transplant, the donor's bone marrow might be considered as foreign body and rejected by recipient's immune system. More the mis-match, higher the chances of rejection. HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) gene sequences the proteins that can lead to this rejection and hence it is important to match the immune signature of potential donor(s) with that of recipient.
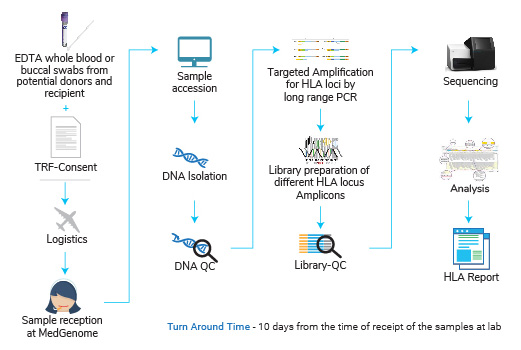
HLA typing test has to be performed on the samples from recipient and donor(s). 50% or higher match in the HLA gene allelic sequence indicates that such a transplant will have least possibility of graft versus host disease or in other words lowest risk of a transplant rejection.