What is a Carrier Screening Test?

When a couple is planning for a pregnancy, it is important that they know all they can about the health of their future family. With state-of-the-art technology, high detection rates, and an unparalleled service model, the Claria Carrier Screening Test from MedGenome helps couples understand and plan better for their future. This is a comprehensive screening test that screens for genetic disorders and has the power to detect disease causing mutations in over 2000 genes. Claria Carrier Screening Test is based on the best-in-class NGS (Next Generation Sequencing) and MLPA (Multiplex Ligation Probe Amplification) technologies and provides the most accurate and comprehensive information needed when a couple is preparing for their pregnancy.

Prevalence
Over 5,00,00,000 people with single-gene disorders
Over 10,00,000 babies born with genetic disorders each year
20% to 30% of all infant deaths are due to genetic disorders
1 in 100 babies born with an inherited disease
Most Common Genetic Disorders
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
- Beta Thalassemia
- Sickle Cell Anaemia
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy
X-linked Recessive Disorders
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Haemophilia A/B
- Hunter Syndrome
- G6PD Deficiency
- X-Linked Mental Retardation
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
If both parents are carriers
- 25% chance of the baby being unaffected
- 25% chance of the baby being affected
- 50% chance of the baby being a carrier
If only one parent is a carrier
- 50% chance of the baby being unaffected
- 50% chance of the baby being a carrier
If one parent is affected and the other parent is a carrier
- 50% chance the baby being affected
- 50% chance of the baby being a carrier
X-Linked Recessive Disorders
If the mother is a carrier for a X-linked disorder
- 50% chance of male baby to be affected
- 50% chance of female baby being carrier
Why screen for inherited genetic conditions?

- Each individual harbors an average of 2.8 known severe recessive mutations
- Carriers are usually healthy or unaffected, but they have a risk of passing on their genetic condition to their children. Traditionally, genetic carrier screening tests have been provided to patients based on their ethnic background or family history.
- However, more than 80% of babies born with inherited genetic diseases have no known family history
Who Should Consider Undergoing Carrier Screening Test?

Genetic carrier testing helps determine one’s carrier status and is an important step of the family planning process. The Claria Carrier Screening Test is recommended for all couples who are planning a pregnancy. But this test is strongly recommended in the following cases:
- Consanguineous marriage
- Either partner is affected by a hereditary disorder
- History of a genetic disorder in the family
- History of multiple pregnancy losses
- A couple from an ethnic group with a high carrier rate of certain genetic disorders
- Congenital anomalies detected in children
When should a couple get tested?
A couple can get tested in the following situations:
- Preconception — when the couple is planning for a baby
- Prenatal Diagnosis (early pregnancy) — check history of the previous child with the disease to diagnose the present pregnancy
- Before an IVF procedure
- Before a Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (embryo selection)
- Before the use of donor sperm and/or oocyte
How do we test for these disorders?
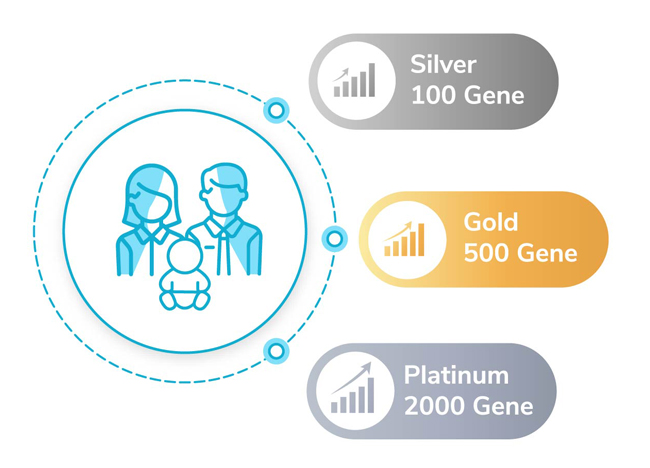
The Claria Carrier Screening Test is based on Next-generation Sequencing (NGS) and Multiplex Ligation Probe Amplification (MLPA) technologies. This enables one to detect disease-causing mutations in over 2,000 genes which are responsible for the Autosomal Recessive and X-Linked Recessive genetic disorders. Next Generation Sequencing is a superior technology which is used to detect all common and rare disease-causing mutations while MLPA is used to detect deletion and duplication in specific genes (SMN, DMD, CYP21A2). Our team of experts adhere to the recommendations of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). With three different panels available (Silver, Gold, and Platinum), the Claria Carrier Screening test offers the option of selecting the version that is best suited to the couple or family.
Next Generation Sequencing vs Genotyping
| Genotyping | NGS | |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Used by many companies for routine carrier screening | Used by a few providers to comprehensively evaluate the gene |
| Mutation detection | Tests for a limited set of common mutations | Tests for 5 to 10 times more pathogenic mutations, and detects all common and rare disease-causing mutations |
| Accuracy | Provides limited utility beyond Caucasian and Jewish ethnicities | Delivers high accuracy across ethnicities |
| Detection of new pathogenic mutations | Fails | Enables the discovery of rare and novel mutations in a pan-ethnic population |
| Fails | Low residual risk, regardless of ethnicity |
Why trust the Claria Carrier Screening Test?
The Claria Carrier Screening Test screens for genetic variations and diseases that are very specific to the Indian population. This unique test is based on the NGS technology and leverages the Indian population genetic variant. This has enabled in developing a highly focused and cost-effective test to screen for diseases and genetic variations that are very specific to the Indian population.
- Best in class accuracy and easy interpretable reporting
- Detection of all known common and rare disease-causing mutations
- Expert genetic counselling sessions with certified, multilinguistic genetic counselors
- The option of three customized screening panels covering over 2,000 genes associated with AR/XLR disorders
- State-of-the-art labs based out of India, to process all samples with immediate access to the status of the sample
- Higher accuracy and low residual risk, regardless of ethnicity
- Pan-India presence for easy sample collection
- Turnaround time of just 14 days for Silver and Gold and 21 days for the Platinum panel
The Test Process
TRF
Physician orders the test
Sample
Blood sample collected
Testing
Samples are shipped to our facility and analyzed
Reporting
Results sent to the physician in 14 to 21 days
Counselling
Our genetic counsellors answer questions and provide additional resources
FAQ
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
- Beta Thalassemia
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy
X-linked Recessive Disorders
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Haemophilia A/B
- Hunter Syndrome
- G6PD Deficiency
- X-Linked Mental Retardation
A carrier is a person who has inherited a recessive variant gene for a genetic trait or mutation but does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. Carriers are, however, able to pass the allele on to their offspring, who may then express the genetic disorder if they inherit the recessive allele from both parents. The chance of two carriers having a child with the disease is 25%. This phenomenon is a direct result of the recessive nature of many genes.
Each individual harbors an average of 2.8 known severe recessive mutations. Carriers are usually healthy or unaffected; but, they have a risk of passing on their genetic condition to their children. Traditionally, genetic carrier screening tests have been provided to patients based on their ethnic background or family history. However, more than 80% of babies born with inherited genetic diseases have no known family history.
- Detect all known common and rare disease-causing mutations
- Reduce the incidence of disease with preconception carrier screening for pathogenic gene mutations and genetic counseling
- Use best in class accuracy and easily interpretable reporting
- Make informed decisions
- Cover 1300 unique conditions with three customized screening panels on NGS and MLPA
- Ensure higher accuracy and low residual risk, regardless of ethnicity
- Shorten turnaround time of just 14 to 21 days
- Remove unnecessary testing
- Reduce the genetic disorder burden
 Enquire
Now
Enquire
Now 
