
Advanced Newborn Screening portfolio
Secure the baby from the impact of inherited metabolic disorders
What is BabySecure, and why is it important?
BabySecure Newborn screening test is a simple genetic test done 24 hours after (not before) a baby is born to identify serious metabolic disorders the baby might have been born with. These disorders, if undetected and untreated, can have adverse consequences for the baby.



Why is this test necessary?
BabySecure is essential because it aids in the early identification of disorders in newborns. Early detection allows for prompt initiation of treatment before the disorder causes harm to the baby.
Who needs to get tested and when do you need to get tested?
Testing is recommended for any newborn after 24 hours of birth, and the test is ideally conducted between 24 to 72 hours after birth. Even if this time window is missed, the test can still be performed. There is no age limit, but the sooner the test is conducted, the better. Early identification of a disorder enables the initiation of treatment at the earliest possible stage.
How is the BabySecure Newborn Screening test performed?
Dried Blood Spot
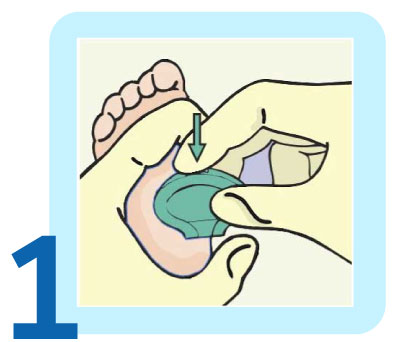
The initial step involves administering a painless heel prick.
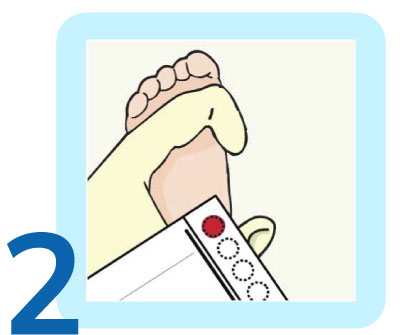
Following the heel prick, a few drops of blood from the baby's heel are carefully placed on a specialized type of filter paper.
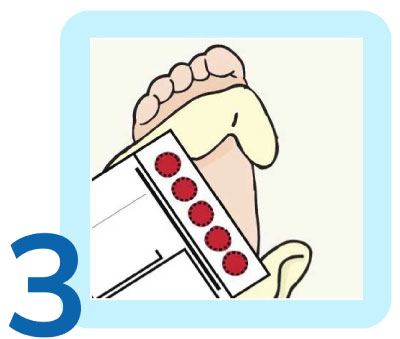
The paper is allowed to dry before being sent to the laboratory, where tests are conducted using Tandem Mass Spectrometry (TMS) and other advanced technologies.
Urine Organic Acid Analysis by GCMS
The GCMS is a simple test done any time after 24 hours of birth of a newborn on an urine sample collected on a dried urine filter paper or Sterile Urine container.
- Urine samples from a newborn can be collected by placing the special filter paper card in the baby’s diaper and checking every 30 minutes, ensuring that the urine is passed and absorbed over the filter. (Figure 1)
- Alternatively, urine sample can be collected in a sterile urine container (10-20 ml) and dipping the special filter paper card. (Figure 2)


Why MedGenome?
Largest CAP-accredited Genomics sequencing lab in South Asia
Best in class accuracy and easy interpretable reporting
Vast coverage of 60+ inherited genetic disorders
Free expert genetic counselling sessions with certified, multilinguistic genetic counselors
Pan-India presence for easy sample collection
Higher accuracy and low residual risk, regardless of ethnicity
Test Details
| Test Code | Test Name | Disorders Covered | Test Description | Turnaround Time (TAT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGM2704 | (Hb+FS+) – BabySecure Newborn Screening (NBS) - comprehensive Panel | 65 | Screening Covers 65 disorders including 55 Metabolic Disorders by Tandem mass spectrometry (TMS), 6 Biochemical (BIO6) and 4 Hemoglobinopathies by other technologies | 24 - 48 Hours |
| MGM2705 | (FS+) – BabySecure Newborn Screening (NBS) - Package 1 | 61 | Screening Covers 61 disorders including 55 Metabolic disorders by Tandem Mass spectrometry and 6 Biochemical (BIO6) disorders by other technologies | 24 - 48 Hours |
| MGM3297 | Urine GCMS 100+ Disorders | 100+ | Screening Covers 100+ disorders in Urine Organic Acid Analysis by GCMS | - |
| MGM3298 | BabySecure Newborn Screening Duo | 100+ | NBS Duo - DBS Amino acid / Acylcarnitine profile by TMS and Urine Organic Acid Analysis by GCMS | - |
BabySecure Newborn Screening Panels
| Disorders covered in BabySecure+ by GCMS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Amino Acidopathies and Organic Acidemias | ||
| 1 | 2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria | ||
| 2 | 2-ketoadipic aciduria | ||
| 3 | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA-lyase deficiency | ||
| 4 | 3-Hydroxyisobutyryl CoA Deacylase Deficiency | ||
| 5 | 3-methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase deficiency | ||
| 6 | 3-methylglutaconic aciduria Type I | ||
| 7 | 5-oxoprolinuria (Pyroglutamic aciduria) | ||
| 8 | Alkaptonuria | ||
| 9 | Aminoacylase I Deficiency | ||
| 10 | Argininemia | ||
| 11 | Argininosuccinic aciduria | ||
| 12 | Benign hyperphenylalaninemia | ||
| 13 | Beta-Aminoisobutyric Aciduria | ||
| 14 | Profound Biotinidase deficiency | ||
| 15 | Beta-ketothiolase deficiency (BKT) | ||
| 16 | Canavan disease | ||
| 17 | Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase-1 Deficiency | ||
| 18 | Carnosinuria | ||
| 19 | Citrullinemia Type 1 | ||
| 20 | Citrullinemia type II | ||
| 21 | Cystinuria | ||
| 22 | Cystathioninuria | ||
| 23 | Defects of biopterin cofactor regeneration. (BIOPT REG) | ||
| 24 | Dihydrolipoyl Dehydrogenase (E3) Deficiency (also known as MSUD Type 31) | ||
| 25 | Familial Renal iminoglycinuria | ||
| 26 | Formiminoglutamic aciduria | ||
| 27 | Glutaric aciduria type II | ||
| 28 | Glutaric aciduria type I | ||
| 29 | Glutathionuria | ||
| 30 | Hartnup Disease | ||
| 31 | Hawkinsinuria | ||
| 32 | Hyperornithinemia-hyperammoninemia- hyperhomocitrullinermia (HHH) syndrome | ||
| 33 | Histidinuria | ||
| 34 | Histidinemia | ||
| 35 | Homocystinuria | ||
| 36 | Hyperprolinemia type 1 | ||
| 37 | Hyperprolinemia type II | ||
| 38 | Hydroxylysinuria | ||
| 39 | Hyperhydroxyprolinemia | ||
| 40 | Hyperleucine-isoleucinemia | ||
| 41 | Hyperglycinuria (Ketotic) | ||
| 42 | Hyperglycinuria (non-ketotic) | ||
| 43 | Hypermethioninemia | ||
| 44 | Hypersarcosinemia | ||
| 45 | Hyperlysinemia Type 1 | ||
| 46 | Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (IBD) | ||
| 47 | Iminoglycinuria | ||
| 48 | Imidazole Amino Aciduria | ||
| 49 | Isovaleric acidemia | ||
| 50 | Lysinuric protein intolerance | ||
| 51 | Malonic acidemia | ||
| 52 | Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) | ||
| 53 | Methylmalonic aciduria, cblA and cblB forms | ||
| 54 | Methylmalonic acidemia and Homocystinuria -СЫ С, D | ||
| 55 | Methylmalonic semialdehydede hydrogenase deficiency | ||
| 56 | Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase deficiency (MUT) | ||
| 57 | Mevalonic aciduria | ||
| 58 | Multiple carboxylase deficiency | ||
| 59 | N-Acetylglutamate Synthetase Deficiency | ||
| 60 | NICCD | ||
| 61 | Ornithine Trans Carbamylase Deficiency | ||
| 62 | Phenylketonuria (PKU) | ||
| 63 | Propionic acidemia | ||
| 64 | Saccharopinuria (also known as Hyperlysinemia Type II) | ||
| 65 | Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency | ||
| 66 | Tyrosinemia caused by liver dysfunction | ||
| 67 | Transient neonatal tyrosinemia | ||
| 68 | Tryptophanuria with dwarfism | ||
| 69 | Tyrosinemia Type II | ||
| 70 | Tyrosinemia Type III (also covers transient neonatal tyrosinemia) | ||
| 71 | Tyrosinemia Type I | ||
| 72 | Valinemia | ||
| 73 | Xanthurenic aciduria | ||
| B | TCA Cycle/Mitochondrial Abnormality | ||
| 74 | Fumarate hydratase deficiency | ||
| 75 | Leigh syndrome | ||
| 76 | Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency | ||
| 77 | Pyruvate decarboxylase deficiency | ||
| 78 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1) deficiency | ||
| 79 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase deficiency | ||
| C | Disorders of Fatty Acid Metabolism | ||
| 80 | Dicarboxylic aminoaciduria | ||
| 81 | Ethyl Malonic Aciduria | ||
| 82 | Glycerol Kinase Deficiency | ||
| 83 | Medium chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency | ||
| 84 | Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency | ||
| 85 | Very Long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. deficiency | ||
| 86 | Short chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase dehydrogenase deficiency | ||
| D | Peroxisomal Disorders | ||
| 87 | Infantile refsum disease | ||
| 88 | Neonatal Adrenoleukodystrophy | ||
| 89 | Primary hyperoxaluria Type 1 | ||
| 90 | Primary hyperoxaluria Type 2 | ||
| 91 | Zellweger syndrome | ||
| 92 | Zellweger like syndrome | ||
| E | Disorders of Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism | ||
| 93 | Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency | ||
| 94 | Dihydropyrimidinase Deficiency | ||
| 95 | Hyperuric acidemia | ||
| 96 | Lesch-Nyhan syndrome | ||
| 97 | Molybdenum cofactor deficiency | ||
| 98 | Orotic aciduria | ||
| 99 | Partial deficiency of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase | ||
| 100 | Thymine Uraciluria | ||
| 101 | Xanthinuria (Type I & II) | ||
| F | Disorders of Sugars | ||
| 102 | D-glyceric aciduria | ||
| 103 | Endogenous sucrosuria | ||
| 104 | Fructose-1 and 6-diphosphatase deficiency | ||
| 105 | Fructosuria | ||
| 106 | Galactokinase deficiency (GALK) | ||
| 107 | Galactose epimerase deficiency (GALE) | ||
| 108 | Lactic Acidosis | ||
| 109 | Transient Galactosemia | ||
| G | Non-IEM Disorder | ||
| 110 | Neuroblastoma | ||
FAQs
These disorders are inherited and cannot be prevented but they are treatable. Even healthy looking babies and those with no family history of such disorders may have them. If a baby is born with a disorder, early detection and treatment is the only solution. Failure to start the treatment in time may result in serious consequences.
The first step is to make a painless heel prick. A few drops of blood from the baby’s heel are then placed on a special type of filter paper. The paper is allowed to dry and is then sent to the lab where tests are performed using Tandem Mass Spectrometry (TMS) and other technologies.


 Enquire
Now
Enquire
Now