What is Syndrome Evaluation System?

A patented technology that comprises of rapid multiplex amplification and accurate identification of the virulence associated genes of the causative agents or organisms. This amazingly fast and accurate platform transcends all conventional diagnostic tests and helpful when organisms are difficult to cultivate or difficult to find. The technologies currently available for diagnosis of infections are grossly inadequate to detect early during the illness and to institute specific therapy in critical illnesses, resulting in loss of function or even loss of life. The amplification of the gene allows for higher sensitivity of the test and the re-naturation of the amplified signature gene to its chemically identified complementary gene sequence on the SES allows for higher specificity of the test. And the simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens allows for early diagnosis of the infection and initiation of therapy.

Prevalence

- According to WHO, 1 in 10 patients get infection while receiving care globally
- The burden of HAI (healthcare associated infection) is several folds higher in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income ones
- Globally, more than 50% of surgical site infections can be antibiotic resistant. In low-and middle-income countries, 11% of patients who undergo surgery are infected in the process
- Infections of the central nervous system (CNS) pose a unique challenge due to high level of morbidity and mortality that they cause as well as the inherent difficulties involved in their diagnosis and treatment. These infections are meningitis, encephalitis, and brain abscesses, and they tend to cause more morbidity and mortality on an average than the infections involving the other organ systems
Common Disorders
Meningitis
- Meningitis is a disease caused by the inflammation of the protective coverings of the brain and spinal cord known as meninges. The infection of the fluids surrounding the brain and spinal cord leads to inflammation of meninges. Globally, meningitis is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in the pediatric population accounting for about 180,000 deaths annually. Studies from India have attributed pneumonia and meningitis as the leading causes of deaths among children below five years of age accounting together to nearly 22.0% deaths.
Acute Encephalitis Syndrome
- Acute encephalitis syndrome (AES) is characterized by an acute onset of fever and clinical neurological manifestation that includes fits, disorientation, behavioural changes, confusion, drowsiness delirium or coma. The causative agent of AES varies with season and geographical location, and predominantly affects population below 15 years. Keeping in mind the wide range of causal agents and the rapid rate of neurological impairment due to pathogenesis, it poses a challenge of rapid diagnosis and early institution of appropriate therapy.

Why do you need the test?
Molecular detection by amplification and hybridization of nucleic acids as a technology has opened a new and innovative era for microbial diagnosis. The use of nucleic acid detection for the diagnosis of infectious diseases in clinical laboratories is facilitated by PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), This approach is useful to detect mutations associated to drug resistance directly on biological samples without the requirement of culturing organism.
When do you need to get tested?
The treating clinician can send the sample to understand the causative organism at the start of the therapy. Additionally, once the treatment has started, based on the test result, the clinician can decide on antibiotic de-escalation or understanding the drug resistance patterns in the difficult-to-treat infections.
Who needs to get tested?
- A patient suffering from infection of CNS where the treatment has to be started based on accurate diagnosis of the causative micro-organism
- To further sharpen the empirical therapy, in case the treatment has already started. This is applicable for patients who are not responding to the empirical therapy- to add antibiotics for effective outcome and also for patients where the empirical therapy is working- to reduce the usage of antibiotics that are not required
- Patients where the treatment is not working due to antibiotic resistance, antibiotic resistance markers can be analysed
Why MedGenome?
Syndrome Evaluation System, which is a patented technology of XCyton Diagnostics, poses unique benefits in terms of treatment of infectious diseases as below:
SES Advantage
| Rapid | Sample to report in 7 – 10 hours |
|---|---|
| Higher Accuracy | Detects more number of cases than conventional methods ( 75% by SES vs 10-15% conventional method) |
| Cost effectives | Avoids multiple testing and unnecessary investigations and reduces ICU stay & associated cost. |
| Provides Direct evidence for the presence of infection | Detects DNA of pathogens |
| Comprehensive | Detects fungi, viruses, parasites and bacteria in a single test. It also detects uni-microbial or poly-microbial infections |
| Rules in or Rules out infections | |
SES Pan CNS
| Microbe Type | Microorganism |
| Leading Bacteria | Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Neisseria meningitidis Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| Gram Positive Bacteria | Staphylococcus aureus Group B Streptococcus Enterococcus spp. Streptococcus pyogenes |
| Gram Negative Bacteria | Klebsiella pneumoniae E.coli Enterobacter spp Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acinetobacter baumannii Bacteroides fragilis Leptospira Salmonella spp. Proteus mirabilis |
| Fungi | Cryptococcus neoformans Aspergillus spp. Candida spp. |
| DNA Viruses | Herpes Simplex Virus 1 & 2 Cytomegalovirus Varicella Zoster Virus Human Herpes Virus-6 John Cunningham Virus |
| Parasite | Toxoplasma gondii |
| Sample Type : Whole Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | |
SES AES
| Microbe Type | Microorganism |
| Leading Bacteria | Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Neisseria meningitidis Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| Fungi | Cryptococcus neoformans |
| DNA Viruses | Herpes Simplex Virus 1 & 2 Cytomegalovirus Varicella Zoster Virus Human Herpes Virus-6 John Cunningham Virus |
| RNA Viruses | JEV Dengue 1-4 West Nile Enteroviruses Chikungunya Rabies Chandipura Measles Mumps Rubella Nipah |
| Parasite | Toxoplasma gondii |
| Sample Type : Whole Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | |
SES Meningitis
| Microbe Type | Microorganism |
| Leading Bacteria | Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Neisseria meningitidis Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| Gram Positive Bacteria | Staphylococcus aureus Group B Streptococcus Enterococcus spp. Streptococcus pyogenes |
| Gram Negative Bacteria | Klebsiella E.coli Enterobacter spp Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acinetobacter baumannii Bacteroides fragilis Leptospira Salmonella spp. Proteus mirabilis |
| Fungi | Cryptococcus neoformans Aspergillus spp. Candida spp. |
| Sample Type : Whole Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | |
SES Encephalitis- Sporadic
| Microbe Type | Microorganism |
| Leading Bacteria | Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Neisseria meningitidis Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| DNA Viruses | Herpes Simplex Virus 1 & 2 Cytomegalovirus Varicella Zoster Virus Human Herpes Virus-6 John Cunningham Virus |
| Fungi | Cryptococcus neoformans |
| Parasite | Toxoplasma gondii |
| Sample Type : Whole Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | |
SES Encephalitis- Outbreak
| Microbe Type | Microorganism |
| RNA Viruses | JEV Dengue 1-4 West Nile Enteroviruses Chikungunya Rabies Chandipura Measles Mumps Rubella Nipah |
| Sample Type : Whole Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | |
| SES Antibiotic resistance markers |
|---|
ESBL: Detects genes that confers resistance to Extended Spectrum Beta Lactams Carbapenem: Detects both, Betalactamases and Metallo Betalactamases NDM-1: Detects New Delhi Metallo Betalactamases Van A: Detects resistance to Vancomycin and Teicoplanin Van B: Detects resistance to Vancomycin (Teicoplanin Sensitive) Methicillin: Detects resistance to Methicillin |
FAQ

- Whole Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)- 1-2 mL
Acceptance Criteria of Sample
- Whole Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Freshly collected whole CSF samples
- Samples volume greater than 1ml
- Sample collected directly from LP needle into potassium EDTA vacutainer
Rejection Criteria of Sample
- CSF samples stored for more than 24 hours
- CSF samples that are spun down (cytospin) to remove WBC
- Samples volume being less than 750 μl
- Sample collected in in-house sterilized injection vials/Falcon tubes/ test tubes or wide mouth Containers
Precaution during sampling
- Sterilise the collection site to prevent skin contaminants getting into the sample
- Collect CSF directly into the vacutainer whose cap is opened, as LP is being per formed. This helps to prevent contamination of sample and avoids transfer of sample
- Analytical sensitivity for viruses is 50 to 250 virions/ml. HSV is detected at 50 virions and CMV is detected at 250 virions. The Sensitivity for bacteria detection is 50-200 cfu / ml
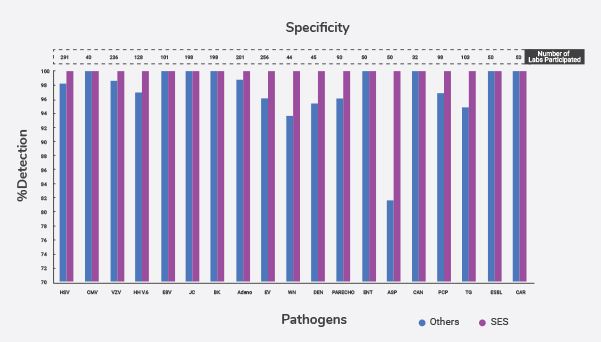
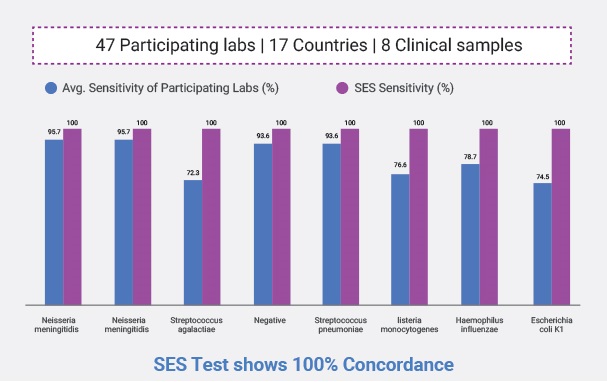
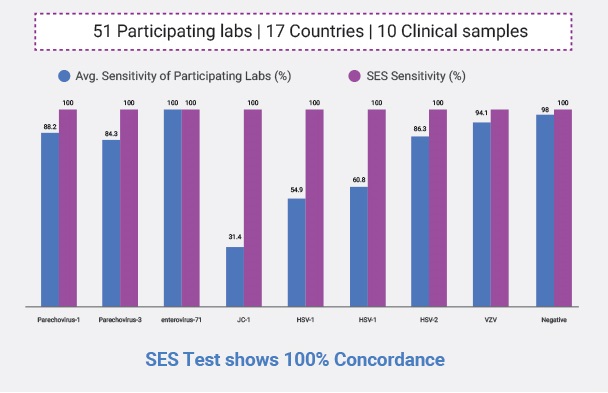
- At laboratory testing Level. We participate in International External Quality Assessment Program by a European Union Notified body called QCMD and our sensitivity for all organisms is 100% except for HHV-6 (90%)
- Clinical Sensitivity: We detect 54 to 72% of cases as can be seen in our publications. These patients were treated for more than 3 days before the sample was sent to us
- At the analytical Specificity Level: We have no interference of one organism with the other when blood is spiked with multiple organisms. Because we identify the amplified product by sequence specific hybridization specificity of the technology is robust
- At Laboratory Level: QCMD testing we never identified even a single negative sample as positive and is 100% specific
- Clinical Specificity: In our study with NIMHANS – wherever we got positives and other methods did not detect the pathogen, we confirmed by sequencing of the amplified products
- At the lab level XCyton has done about 80,000 tests in house before testing human samples. NIMHANS validated the neuro-infection panels. While sepsis panels were validated in a Randomized Controlled Trial(RCT) at JIPMER, Pondicherry. It was compared with culture in adult patients at Fortis Hospital Noida and Fortis Hospital Bangalore on Leukemia patients with Febrile neutropenia
- There are 26 National International publications on the clinical use of SES. 18 of them were from clinicians who independently published their results
- In acute illnesses such as Sepsis, Febrile Neutropenia, Pneumonia, Meningitis and encephalitis body fluids contain live bacteria, bacteria damaged by human immune system, bacteria damaged by antibiotics and dead bacteria. There is a dynamic equilibrium among all these forms. Only live thriving bacteria will be detected by culture. Other forms are not. As a result, the detection rate by SES is several folds higher than culture
- With your clinical judgment, you save about 52% of sepsis cases. That result matches the best of the West. However, culture detects about 15% of ICU cases while SES can detect 55% to 75% of cases. When you know the pathogen early you can save significant portion of 48% of the cases, currently being lost


 Enquire
Now
Enquire
Now