What is KaryoSeq Test?
KaryoSeq is a genetic test that utilizes low pass Whole Genome Sequencing for detection of Aneuploidies of all chromosomes and Copy Number Variations (deletions and duplications) >1 Megabase.


Prevalence
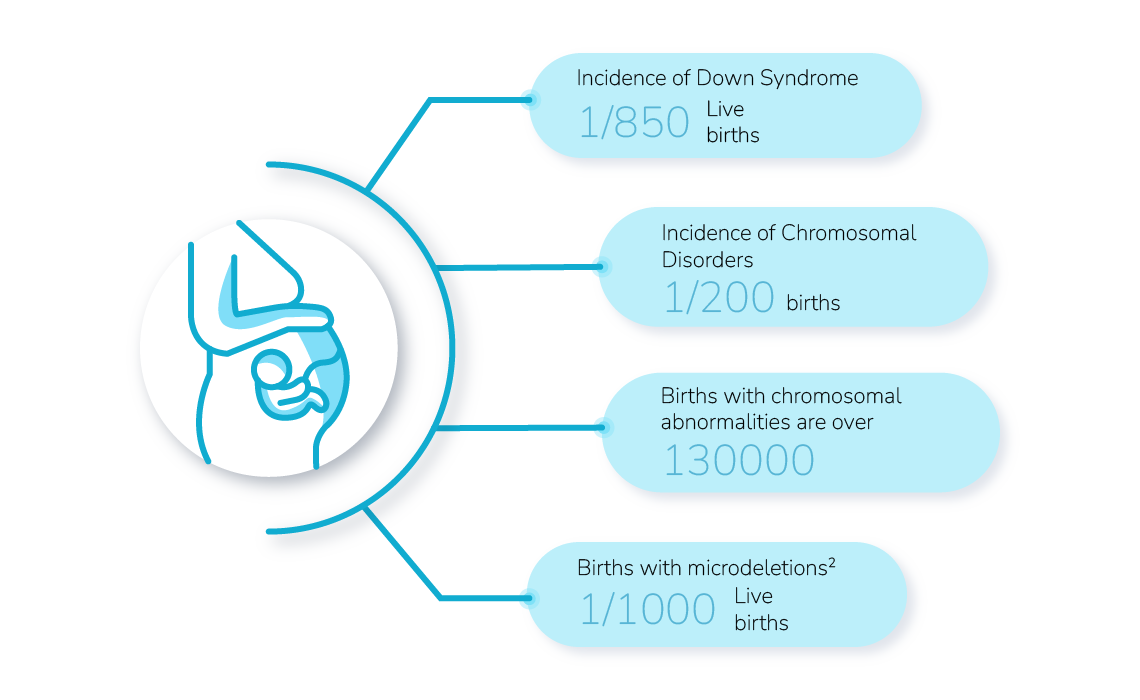

chromosomal abnormalities increase with age.
The Risk of having a Baby with Down Syndrome1
Risk: 1 in 1300
Risk: 1 in 270
the risk for a clinically significant microdeletions exceeds the risk for Down Syndrone.
Why do you need KaryoSeq Test?
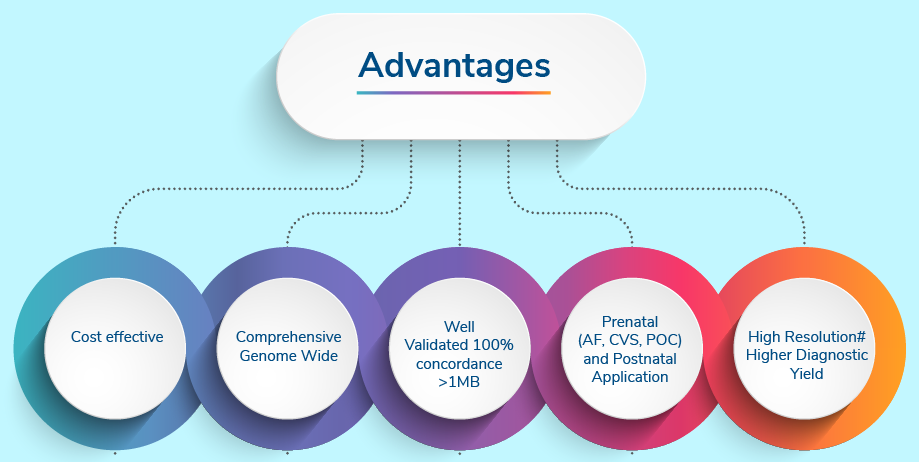
This is a cost-effective test for identifying aneuploidies of any chromosome as well as copy number variations above 1 Mb.
Applicable for Conditions like:
Any situation that calls for confirmation of a suspected aneuploidy such as trisomy 21, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, Monosomy X or other situations where a possible deletion or duplication is suspected, both in prenatal and postnatal cases.

When do you consider getting tested for the KaryoSeq Test?
Prenatal
High risk on maternal serum screening, abnormal ultrasound, family history of chromosomal abnormality, any structural abnormality, miscarriage (products of conception)
Post Natal
Patients with multiple congenital anomalies, autism/autism spectrum disorders (ASDs), and suspected chromosomal imbalances, including micro-deletion syndromes, require specialized care.
Validation
The validation process involved comparison of the CMA results with KaryoSeq.
Sample Size
- 10 normal
- 138 abnormal
DNA Sample Type
- Amniotic Fluid
- Chorionic villus biopsy
- Product of conception
- Direct fetal DNA
- Peripheral blood DNA
Aberrations Identified
- Whole chromosome aneuploidies
- CNVs
Concordance
- 100% concordance>1Mb CNVs
Here are some CNVs that have been identified
| Sl. No. | Sample Type | Microarray detected CNV’s | Size (Mb) | KaryoSeq Detected CNV’s | Size (Mb) | Concordance (Microarray vs KaryoSeq) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CVS | arr[GRCh38] (18)x3 [Edwards syndrome] | 80.1 | Seq[GRCh37]18p11.32 - q23(0_8,077,248)x3 | 78 | ✓ |
| 2 | CVS | arr[GRCh38] (21)x3 [Down syndrome] | 33.1 | Seq[GRCh37]21p13-q22.3(0-48,129,895)x3 | 78 | ✓ |
| 3 | POC | arr[GRCh38] (12)x3 | 133.5 | Seq[GRCh37]12p13.33 - q24.33(0-133,851,895)x3 | 133.8 | ✓ |
| 4 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38]11p15.5q23.3(230,616_116,744,147)x3, arr[GRCh38]22q11.1q11.21(16,408,174_20,291,006)x1 [DiGeorge syndrome] | 116.5 3.88 | Seq[GRCh37]11p15.5-q23.3(230,616_116,744,147)x3 Seq[GRCh37]22q11.1-q11.21(16,408,174_20,291,006)x1 | 103 4 | ✓ |
| 5 | AF | arr[GRCh38] 15q13.2q13.3(30,820,717_32,622,039)x1 | 1.8 | Seq[GRCh37]15q13.2-q13.3(30,885,000_32,485,000)x1 | 1.02 | ✓ |
| 6 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 5q35.2q35.3(175,989,093_178,055,505)x1 | 2.0 | Seq[GRCh37]5q35.2 - q35.3(75,568,094_177,768,094)x1 | 2.2 | ✓ |
| 7 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 22q13.32q13.33(48,199,706_50,759,338)x1 [Phelan-McDermid syndrome] | 2.5 | Seq[GRCh37]22q13.32 - q13.33(48,470,380_51,304,566)x1 | 2.8 | ✓ |
| 8 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 22q11.21(18,950,000_21,108,369)x1 [DiGeorge syndrome] | 2.1 | Seq[GRCh37]22q11.21(18,762,659_21,870,380)x1 | 3 | ✓ |
| 9 | POC | arr[GRCh38]Yq11.23(25,519,063_26,318,566)x2 Yq11.223q11.23(23,717,662_24,887,532)x2 | 1.1 0.8 | Seq[GRCh37]Yq11.223 - q11.23(124,655,552_28,476,607)x2 | 3.8 | ✓ |
| 10 | AF | arr[GRCh38] 9q22.1q22.31(87,988,200_92,870,072)x1 | 4.8 | Seq[GRCh37]9q22.1-q22.31(90,521,336_95,971,336)x1 | 5.4 | ✓ |
| 11 | POC | arr[GRCh38] 10q22.3(79,625,681_80,213,053)x1, arr[GRCh38]15q11.2q13.1(23,102,621_28,458,904)x1 [Angelman syndrome/ Prader-Willi syndrome] | 0.6 5.3 | Seq[GRCh37]10q11.22(18,762,659_21,870,380)x1 Seq[GRCh37]15q11.2 - q13.1(18,762,659_21,870,380)x1 | 3.3 5.1 | ✓ |
| 12 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 18q21.2q21.33(54,720,552_62,003,701)x1 | 7.2 | Seq[GRCh37]18q21.2 - q21.33(52,309,136_59,709,136)x1 | 7.4 | ✓ |
| 13 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 13q32.3q34(101,067,948_114,342,258)x1, arr[GRCh38]16p13.3p13.2(35,881_8,831,829)x3 | 13.2 8.7 | Seq[GRCh37]13q33.1-q34(101,770,197_115,169,878)x1 Seq[GRCh37]16p13.3-p13.2(5,260,000_8,910,000)x3 | 13.3 3.6 | ✓ |
| 14 | AF | arr[GRCh37] 10p15.3p14(100,048_7,701,527)x1 | 7.6 | Seq[GRCh37]10p15.3-p14(0_7,660,000)x1 | 10 | ✓ |
| 15 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 2q12.3q13(108,652,368_110,116,258)x1 | 1.2 | Seq[GRCh37]2q12.3 - q13(109,200,000_111,051,337)x1 | 1.4 | ✓ |
| 16 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 21q11.2q21.3(13,644,166_25,925,065)x1 | 12.2 | Seq[GRCh37]21q11.2 - q21.3(15,500,000_26,800,422)x1 | 11.3 | ✓ |
| 17 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 8q24.21q24.3(130,350,392_145,070,385)x3 | 14.7 | Seq[GRCh37]8q24.21-q24.3(131,400,277_144,250,277)x3 | 12.9 | ✓ |
| 18 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38]5p15.33p15.2(113,462_13,788,173)x1 [Cri du chat syndrome] arr[GRCh38]20p13p12.1(80,929_15,514,914)x3 | 13.7 15.5 | Seq[GRCh37]5p15.33 - p15.2(0_13,810,000)x1 Seq[GRCh37]20p13 - p12.1(0_13,810,000)x3 | 13.8 15.6 | ✓ |
| 19 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 16p11.2(29,568,701_30,166,595)x1 | 0.5 | Seq[GRCh37]16p11.2 - q11.2(31,910,000_46,800,515)x1 | 14.8 | ✓ |
| 20 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 7p21.3p15.2(10571965-26444007)x1 | 15.8 | Seq[GRCh37]7p21.3 - p15.2(10,560,000_26,460,000)x1 | 15.9 | ✓ |
| 21 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 13q22.2q31.3(75,664,252_91,427,209)x1 | 15.7 | Seq[GRCh37]13q22.2 - q31.3(76,120,197_92,110,324)x1 | 16 | ✓ |
| 22 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 9q34.3(137,434,967_138,124,196)x1 | 0.7 | Seq[GRCh37]9p13.1 - q12(38,814,048_55,146,786)x1 | 16.33 | ✓ |
| 23 | Peripheral Blood | arr[GRCh38] 4q34.1q35.2(172,079,686_190,036,305)x1 | 17.9 | Seq[GRCh37]4q34.1 - q35.2(172,981,307_191,154,276)x1 | 18.2 | ✓ |
| 24 | POC | arr[GRCh38] (13)x3 [Patau syndrome] | 95.6 | Seq[GRCh37]13p13.1 - q12(0_115,169,878)x3 | 23 | ✓ |
| 25 | AF | arr[GRCh38]6q26q27(162,350,656_170,610,394)x1, arr[GRCh38]7q33q36.3(133,640,234_159,327,017)x3 | 8.3 25.7 | Seq[GRCh37]6q26-q27(162,025,576_171,115,067)x1 Seq[GRCh37]7q33-q36.3(133,113,445_159,138,663)x3 | 9 26 | ✓ |
| 26 | POC | arr[GRCh37] (19)x1 | 58.6 | Seq[GRCh37]19q13.2(8,404,119_49,024,030)x1 | 40.6 | ✓ |
| 27 | CVS | arr[GRCh38] (20)x3 arr[GRCh38](21)x3 [Down syndrome] | 64.2 33.1 | Seq[GRCh37]20p13 - q13.33(0-63,025,520)x3 Seq[GRCh37]21p13 - q21.2(0_25,800,422)x3; Seq[GRCh37]21q21.2 - q22.3(25,800,422_48,129,895)x3 | 63 25.8 22.3 | ✓ |
| 28 | POC | arr[GRCh38] Xp22.33q28(251,880-156,004,066)x1 [Turner syndrome] | 155.7 | Seq[GRCh37]Xp22.33 - q28(0_149,158,438)x1 Seq[GRCh37]Xq28(:149,158,438_153,908,438)x1 Seq[GRCh37]Xq28(153,908,438_155,270,560)x1 | 149 4.7 1.3 | ✓ |
| 29 | POC | arr[GRCh38] Xp22.33q28(2,785,592_155,691,858)x2[Klinefelter syndrome] | 155.7 | Seq[GRCh37]Xp22.33 - q28(0_155,270,560)x3 | 155.2 | ✓ |
| 30 | CVS | arr[GRCh38]Xp22.33q28(2,785,592_155,691,858)x2[Klinefelter syndrome] | 155.7 | Seq[GRCh37]Xp22.33 - q28(0_155,270,560)x3 | 155.2 | ✓ |
Why Choose Medgenome Labs For Your KaryoSeq Test?
- Well Validated test
- Largest CAP-accredited Genomics sequencing lab in South Asia
Technical Details
It is a low pass Whole Genome Sequencing test and data is analyzed using bioinformatics algorithms.
| Test Code | Test Name | Sample Requirements | TAT | Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGM2754 | Karyoseq (without MCC or other samples) | Peripheral Blood, Direct DNA | 8 Working Days | NGS |
| MGM2777 | KaryoSeq with MCC | Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)/Amniotic Fluid (AF)/Cultured Amniotic Fluid/Cord Blood/Cardiac Blood/Products of Conception Tissue (POC)/Peripheral Blood, Direct DNA/DNA Isolated from Cell Lines or Cultured Cells | 10 Working Days | NGS |
| MGM2761 | Karyoseq with (prenatal cell culture if required) | Chorionic Villus Biopsy, Amniotic Fluid | 8 + 12 Working Days | NGS |
Sample Details

Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)

Amniotic Fluid (AF)

Cultured Amniotic Fluid

Cord Blood

Cardiac Blood
Products of Conception Tissue (POC)

Peripheral Blood, Direct DNA



 Enquire
Now
Enquire
Now