What is Recurrent Pregnancy Loss ?

Recurrent Pregnancy Loss (RPL) is defined as three consecutive pregnancy losses occuring prior to 20 weeks from the last menstrual period1
Prevalence
- RPL is reported in approximately 1% to 2% of pregnant women
- Current techniques can identify up to 50% of couples suffering from RPL2
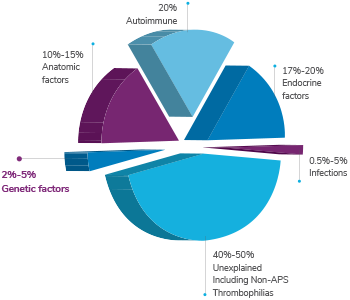
- Genetic causes account for about 2% to 5% of RPL1
- [1] Ford HB, Schust DJ. Recurrent pregnancy loss: etiology, diagnosis, and therapy. Rev Obstet Gynecol 2009;2: 76-83.
- [2] Jaslow CR, Carney JL, KuttehWH. Diagnostic factors identified in 1020 women with two versus three or more recurrent pregnancy losses. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(4):1234–43.

What are the genetic causes of RPL?
- 30% to 50% of all miscarriages are due to cytogenetic reasons3
- 2% to 4% of RPL is associated with a parental balanced structural chromosome rearrangement, most commonly balanced reciprocal or Robertsonian translocations1
- Other reasons include chromosomal inversions, insertions, and mosaicism1
- [3] Ogasawara M, Aoki K, Okada S, et al. Embryonic karyotype of abortuses in relation to the number of previous miscarriages. Fertil Steril. 2000;73: 300–304
Why do you need the test?

Abortion has multiple causes and may involve endocrine, anatomic, immunological, infectious, environmental, and genetic factors. RPL testing can:
- Detect if the pregnancy loss was due to an abnormal chromosome number (aneuploidy)
- Provide information that can be helpful for patients and physicians to understand the cause of the pregnancy loss
- Develop a plan to support a successful pregnancy in the future
When do you need to get tested?

When a couple experiences a second pregnancy loss they can consider getting a RPL test done. This involves testing the products of conception (POC). In addition, parental karyotyping can be done along with an appropriate pre and post-test genetic counselling.
How is the test done?
RPL testing is done by taking a small sample of the POC and checking for chromosomal abnormalities using standard techniques such as Karyotyping and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH).

More advanced methods such as Chromosomal Microarrays(CMA) offer an in-depth analysis of the defect going into microdeletions and microduplications that could have caused the miscarriage.
Advantages of CMA
- Needs no cell culture
- Detects chromosomal deletion/duplications by use of the highly sensitive platform with >99% sensitivity
- Increased whole-genome coverage targeting 396 relevant regions for prenatal analysis (18,018 CNV and 148,450 SNP)
- Increased coverage density (25 markers/100 kb) in 396 empirically selected regions relevant for prenatal research
- Detects low levels of mosaicism in the sample
- Offers a minimum resolution of 1Mb for losses, 2Mb for gains, and 5Mb for LOH/AOH (Loss/Absence of Heterozygosity)
Parental Karyotyping

About 5% of couples with RPL are known to carry Robertsonian translocations and balanced reciprocal translocations. Both the specific chromosome(s) affected, and the types of rearrangement influence the probability of a future live birth. Conventional karyotyping can be used in such cases. This standard method can detect most chromosomal abnormalities. Pre and post-test genetic counselling are essential.4
- [4] Regan L, Backos M, Rai R. 2011. Green-top GuidelineNo 17. The investigation and treatment of couples with recurrent first-trimester and second-trimester miscarriage. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG), London.
Who needs to get tested?
Couples who have:
- Pregnancy loss with fetal abnormalities
- Recurrent pregnancy loss
- Repeated miscarriages while undergoing IVF
RPL workflow
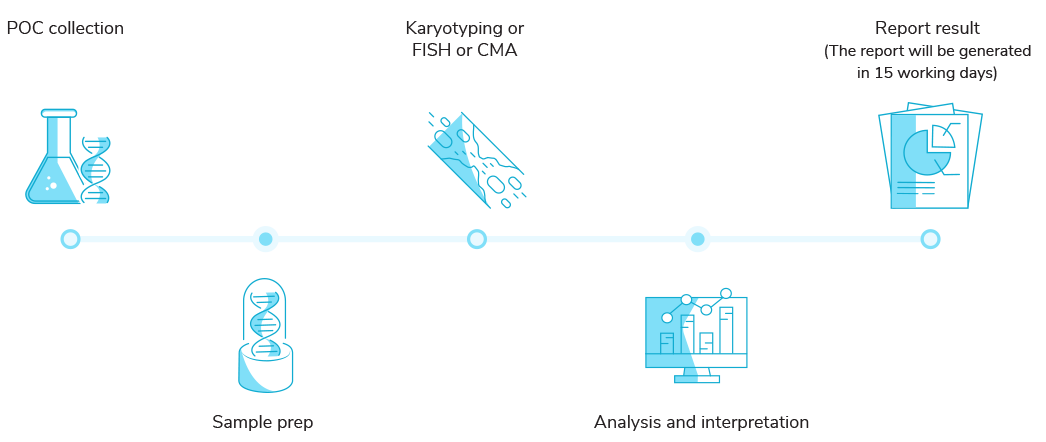
Test Sample Requirement for CMA

Minimum 100 mg of Product of Conception (POC)
Taken in a sterile 15ml falcon tube either in a saline solution + 1% antibiotic or RPM1640 + 10%fbs + 1% antibiotic (Formalin fixed or degraded samples will not be accepted)

Also provide 3ml of maternal whole blood in a EDTA vacutainer for Maternal Cell Contamination check.


 Enquire
Now
Enquire
Now