Tumor Marker Testing Excellence
Quicker, Smarter & Better test for treatment decision
What is TumorTrack Advance?
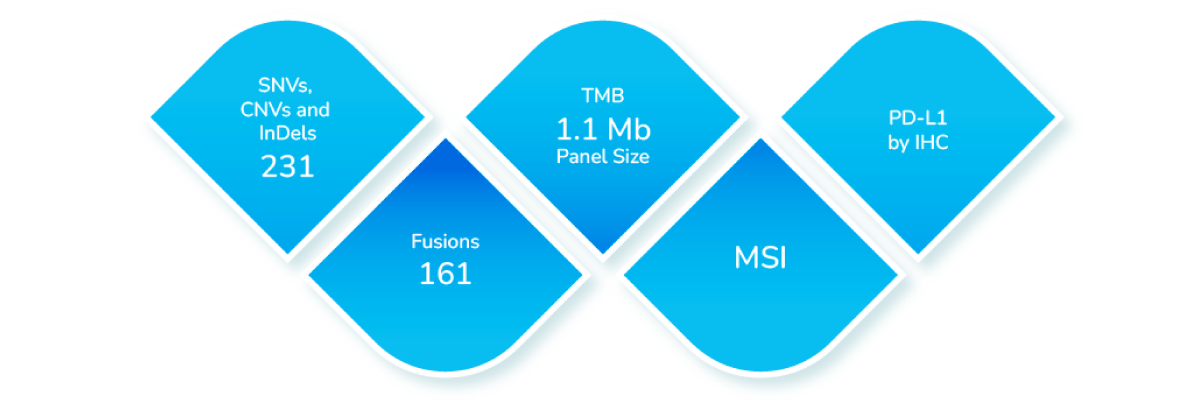
TumorTrack Advance is a next generation sequencing (NGS) assay consisting of DNA and RNA based testing which detects single nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertion-deletion mutations (InDels), copy number variants (CNVs), fusions, tumor mutation burden (TMB), microsatellite instability (MSI) and PD-L1 expression in multiple solid tumors.

Coverage
Coverage of Biomarkers
Lung Cancer

Breast Cancer

Ovarian Cancer

Prostate Cancer
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
Thyroid Cancer

Colorectal Cancer

Melanoma

Bladder Cancer

Uterine Cancer

Pancreatic Cancer

Hepatocellular Carcinomas

Sarcomas

Thymus Cancer

Glioma
Prevalence

- According to ICMR report the number of Indians suffering from cancer is projected to increase to 29.8 million in 2025 from 26.7 million in 2021
- Males are at 9.81% risk to develop cancer before the age of 75 and females at 9.42%
- The most common types of cancer in males include lip, oral cavity, lung, stomach, colorectal, and esophagus, while in females it includes breast, lip, oral cavity, cervix, lung, and gastric cancers (in descending order)
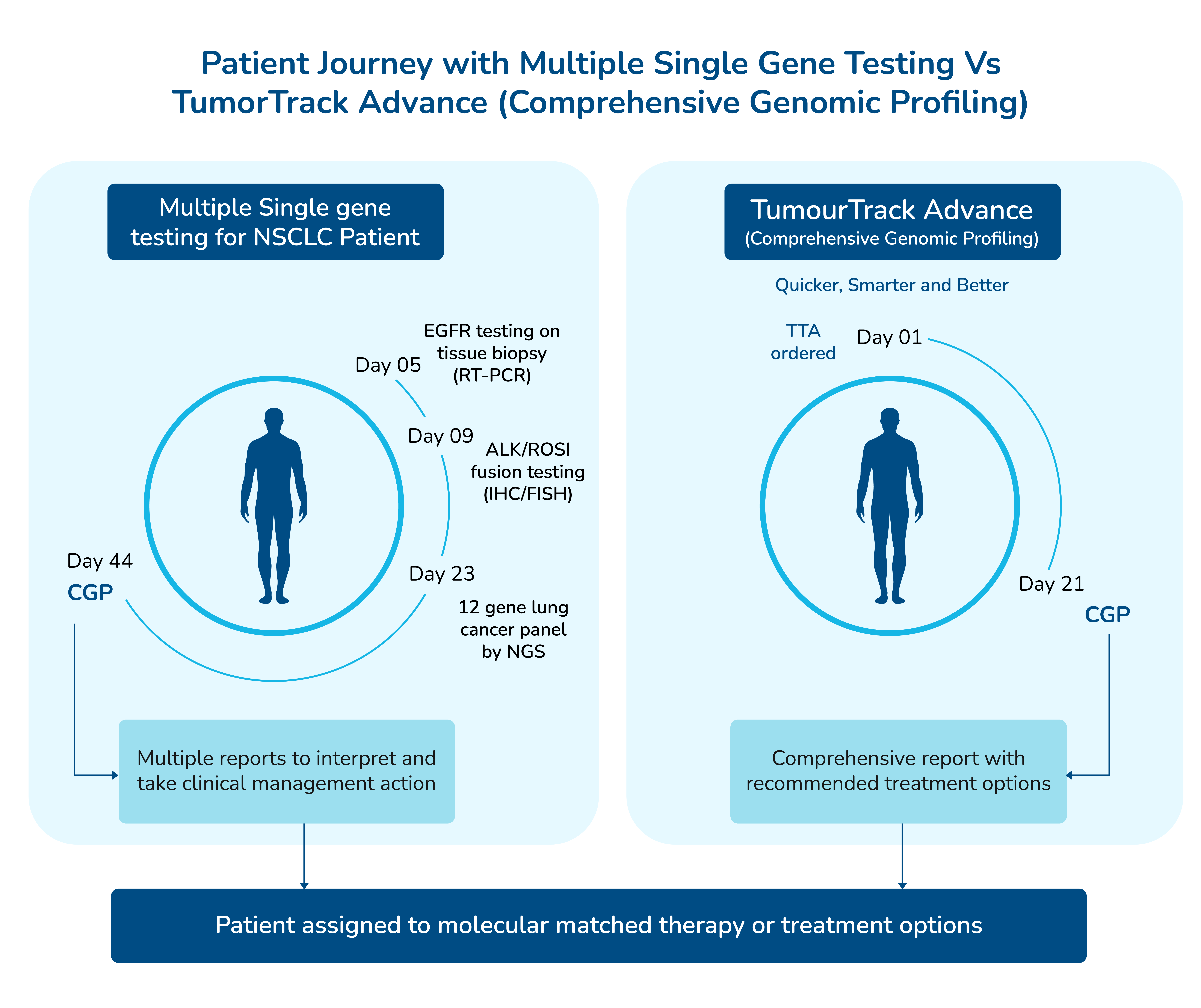
Why you need Tumor panel test?
Single holistic test for the diagnosis, prognosis and to determine treatment options (Targeted Therapy & Immunotherapy)



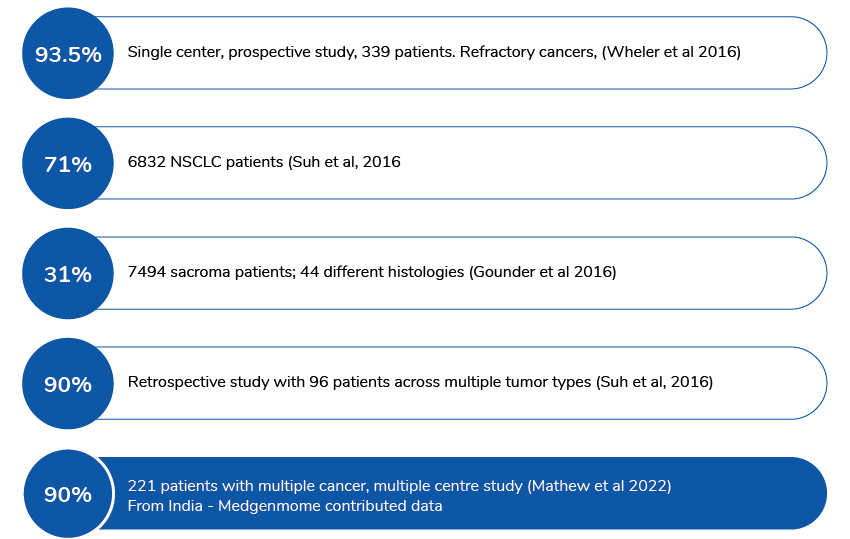
Actionable/Potentially actionable variants identified in cancer patient samples from published data:
Test Details
| Sl No. | Test Code | Test Name | TAT(Days) | Inclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MGM3441 | TumourTrack - Comprehensive Tumor Panel (SNVs, Indels, CNVs and Fusions) (Expedited TAT) | 15 Days | ~400 genes SNVs, Indels, CNVs, Fusions and TMB |
| 2 | MGM3440 | TumourTrack Advance - Comprehensive Tumor Panel + Microsatellite Instability (MSI) test (Expedite TAT) | 15 Days | ~400 genes SNVs, Indels, CNVs, Fusions, TMB and MSI |
| 3 | MGM1879 | TumourTrack - Comprehensive Tumor Panel | 21 Days | ~400 genes SNVs, Indels, CNVs, Fusions and TMB |
| 4 | MGM1785 | TumourTrack Advance - Comprehensive Tumor Panel + Microsatellite Instability (MSI) test | 21 Days | ~400 genes SNVs, Indels, CNVs, Fusions, TMB and MSI |
| 5 | MGM1556 | Tumour Mutation Burden (TMB) analysis by NGS | 14 Days | TMB |
| 6 | MGM196 | Tumour Mutation panel (SNVs, InDels & CNVs) | 21 Days | 231 genes SNVs, Indels, CNVs |
| 7 | MGM3446 | TumorFocus panel by NGS | 14 Days | 77 genes SNVs, Indels, CNVs and Fusions |
Assay specifications
| Cancer type | Specimen | FFPE block requirement* | Tumor Purity Minimum | Limit of detection | Average depth of sequencing | Analytical sensitivity | Analytical specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Solid Tumor Types | FFPE Tissue Block/Cytology Cell Block, Tissue in RNA later* | Cross-sectional tumor area of 25mm2 containing at least 40 μm of tumor tissue | >10% (as determined by Molecular Pathologist) | 5% VAF for SV and InDels >10 Spanning Reads for Fusions >2.5-fold Change for CNV | >250X | 99.15% (SNVs/InDels); 98% Fusions; ≥85-90% (CNVs) | 99.9% |


 Enquire
Now
Enquire
Now